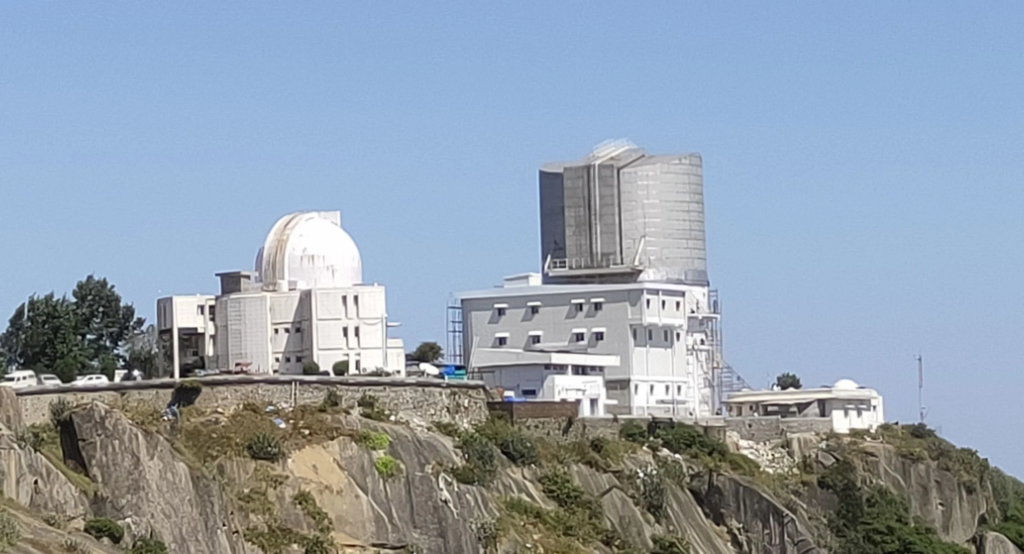
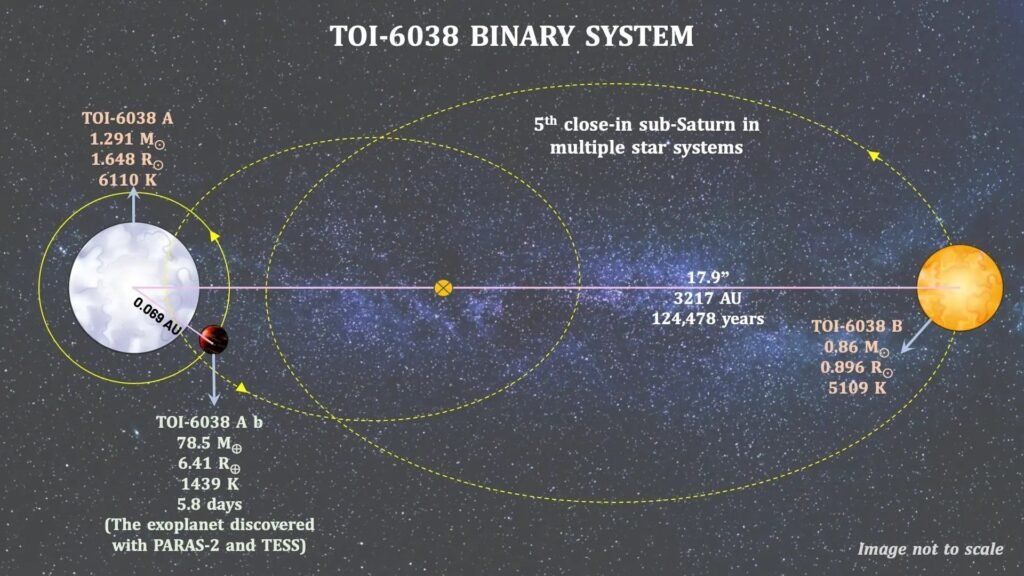
According to a ISRO statement, a team of scientists from the Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad, have discovered a new exoplanet, TOI-6038A b, which is a dense sub-Saturn-sized planet in a wide binary system.
The planet has a mass of 78.5 Earth masses and radius of 6.41 Earth radii, it orbits a bright, metal-rich F-type star every 5.83 days in a circular orbit.
TOI-6038A b lies in the transition region between Neptune-like and gas giant exoplanets, which is classified as a “Sub-Saturn”- a category which is absent in our solar system, making it an unique subject for studying planetary formation and evolution.
Big Achievement For Indian Astronomy
This is the second exoplanet discovery using the advanced PARAS-2 spectrograph, which is attached to the 2.5- meter telescope at PRL’s Mount Abu Observatory in Gurushikhar, Mount Abu.
It is also the fifth exoplanet discovery using the combined efforts of the PARAS-1 and PARAS-2 spectrographs.
The PARAS-2 spectrograph is the Asia’s highest-resolution stabilised radial velocity (RV) spectrograph.
The precise RV data from PARAS-2, along with high-spatial resolution speckle imaging from PRL’s telescope, played a crucial role in confirming the planet’s nature.
Insights Into Planetary Formation And Motion
TOI-6038A b has a high density of 1.62 g/cm3 which places the planet among the denser sub-Saturns.
Scientists believe that the planet formed through unique mechanisms such as high-eccentricity tidal migration (HEM) or early-driven migration.
The planet’s host star, TOI-6038A, is a part of a binary system, with a companion K-type star, TOI-6038B, which is located 3217 AU (Astronomical Units) away.
The presence of this wide binary companion brings a questions about its influence on the planet’s orbit.
“While the companion could influence the planet’s orbit via secular perturbations, initial analyses suggest these effects may not fully explain its close-in orbit,” ISRO said.
TOI-6038A b is only the fifth sub-Saturn exoplanet discovered in a binary system.
Also Read: NASA Reveals Orbit Of Asteroid Could Hit Earth In Year 2032
A Crucial Target For Future Research
After closely analysing the TOI-6038A b’s internal structure is suggests that it has a massive rocky core, which is making up approximately three-fourths (0.75) of its total mass, the remaining mass consisting of a hydrogen-helium envelope.
This provides a key insights into the transition between terrestrial planets and gas giants.
The brightness of the TOI-6038A system makes it an ideal candidate for atmospheric characterisation and spin-orbit alignment studies.
Additionally, further studies and investigations may help scientists understand the forces that shaping its evolution.
Follow Techsgyaan to get more such Science related news.